📜 Journal Club: Methods to monitor respiratory effort during mechanical ventilation
By: Marcelo Alcantara, Médico - 01/08/2026 13:04
🧐 In December 2025, the authors:
Glauco Pens (Respiratory ICU, InCor, University of São Paulo – USP)
Bruno Pinheiro (ICU, University Hospital, Federal University of Juiz de Fora – UFJF, Juiz de Fora, MG, Brazil)
Irene Telias (University Health Network and Sinai Health System – Toronto, Canada)
Eduardo Costa (also from the Respiratory ICU)
📜 Published an elegant and concise “Point of View” article on methods for monitoring respiratory effort during mechanical ventilation in Critical Care Science, the official scientific journal of the Brazilian Association of Intensive Care Medicine (AMIB) and the Portuguese Society of Intensive Care.
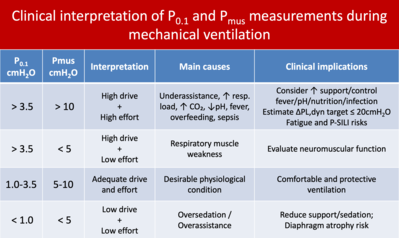
🙂 A very didactic and well-referenced article highlights the importance of estimating ventilatory drive through the measurement of airway occlusion pressure at 100 ms (P0.1), as well as respiratory muscle pressure (Pmus), using techniques such as the Muscle Pressure Index (PMI) and the occlusion pressure swing (ΔPocc), as clearly illustrated in the central figure.
👉🏼 We emphasize the practical application of interpreting P0.1 measurements and estimating Pmus as suggested by the authors, summarized in the table we prepared below.
😉 How have you been assessing ventilatory drive and respiratory muscle effort in your mechanically ventilated patients?
😉 Here is the link to the article — enjoy the read!
To add an answer on this topic and read the replies...
You must have a valid and active xlung subscription
If you are already a subscriber, please Login at the top of the page, or subscribe now