A patient with pulmonary fibrosis and respiratory distress in the pressure support mode (PSV)
Last update: Wednesday, 13 Oct 2021 at 19:46
A 79-yeard-old man with pulmonary fibrosis was admitted in the ICU for acute hypoxemic respiratory failure that required intubation and mechanical ventilation. After some clinical improvement he was lightly sedated and ventilated in the pressure support mode (PSV) with the following settings: PS:8cmH2O, cycling off of 25% of the peak inspiratory flow and PEEP:10cmH2O. The use of accessory muscles of respiration was clinically evident and the curves on the ventilator display are shown bellow.
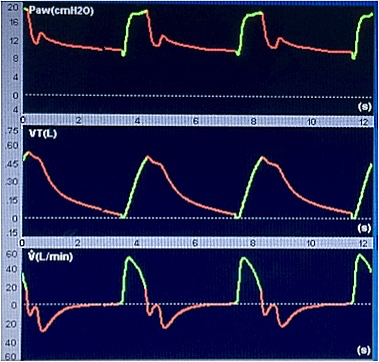
Source: www.xlung.net
Which of the following would be the most appropriate adjustments of the PSV mode?
a) Reduction of the rise time
b) Increase of the rise time
c) Reduction of the cycling off criterion (% peak inspiratory flow)
d) Increase of the cycling off criterion (% peak inspiratory flow)
To continue reading...
You must have a valid and active xlung subscription
If you are already a subscriber, please Login at the top of the page, or subscribe now